|
.
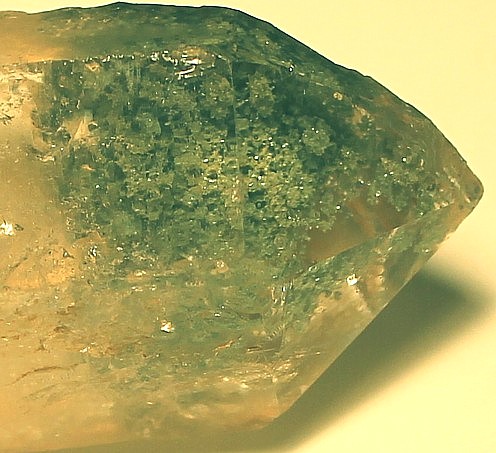
Chlorite Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula:
(Mg,Fe)5Al2Si3O10(OH)8
Magnesium Iron Aluminum
Silicate. The chlorites are a group of phyllosilicate minerals.
Colors:
Green of various shades.
Rarely pale green, yellow, white, rose-red. All group members are
strongly pleochroic in shades of green in green varieties, yellow and
brown in brown varieties, and violet and carmine in rose varieties.
Hardness:
2.0 to 2.5
Density: 2.6
to 2.8
Cleavage:
One perfect parallel to
the base. Similar to the micas in many ways.
Crystallography: Monoclinic
Usually
foliated massive or in aggregates of minute scales; in finely
disseminated particles; earthy.
It is found
in six-sided tabular crystals, with prominent basal planes. Similar in
habit to the crystals of the mica group, but distinct crystals rare.
Luster:.
Vitreous glassy
luster. It is transparent or translucent.
Optics:
(Refractive Index):
= 1.57 to 1.67
|
 |
|
Composition,
Structure and Associated Minerals:
A
common and widespread mineral, always of secondary
origin. It results from the alteration of silicates containing
aluminium, ferrous iron and magnesium, such as pyroxene, amphibole, biotite,
garnet, vesuvianite, etc. To be found where rocks, containing such minerals,
are undergoing metamorphic change. The green color of many igneous rocks is
due to the chlorite into which the ferromagnesian silicates have altered.
The green color of many schists and slates is due to finely disseminated
particles of the mineral. The name chlorite is derived from a Greek word
meaning green, in allusion to the common color of the mineral.
This group of
closely related micaceous minerals is known as the Chlorite Group or as the
chlorites. They are silicates of aluminium with magnesium, ferrous iron and
hydroxyl. Ferric iron may replace the aluminium in small amount. Chromium
and manganese may also occur. Calcium and the alkalies, which are
characteristic of the micas proper, are practically absent. Their
crystal forms
are similar to those of the micas and they show a perfect basal
cleavage. Their laminae, however, are tough and inelastic. Clinochlore is
the most common member of the group.
Identification and Diagnostics
Before the
blowpipe the chlorites exfoliate and fuse with difficulty. Some varieties
whiten. The varieties rich in iron fuse more
readily than those in which there is little iron in some instances to
a black glass. In the closed tube all yield water when strongly heated.
Unattacked by hydrochloric acid. Decomposed by boiling concentrated
sulphuric acid, giving a milky solution. Characterized by its green color,
micaceous structure and cleavage and by the fact that the folia are not
elastic.
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins:
The chlorite group comprises a number of platy hydrous magnesium, aluminium
silicates that appear to be isomorphous mixtures of molecules. Their
composition is too complex
to be represented by any single simple formula. The chlorites are
alteration products of various silicate minerals. They occur as essential
constituents in crystalline schists (chlorite schists / greenschist), and as
the alteration products of silicates in igneous
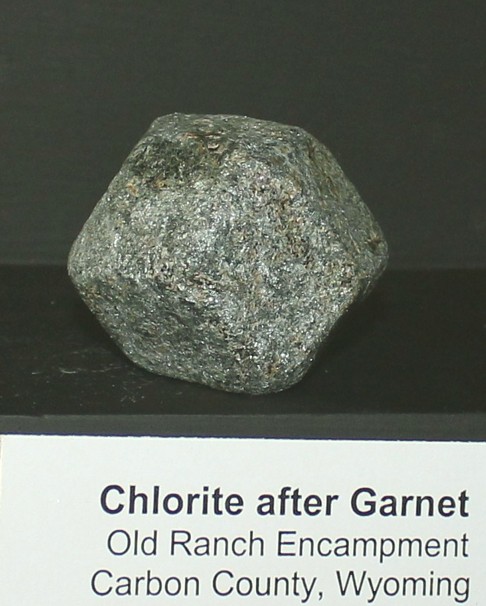
rocks, in which case the latter assume a green color. The chlorites
also form pseudomorphs after garnet, biotite, augite, hornblende, etc., and
sometimes they occur filling little veins cutting through altered rocks.
Corundophilite is frequently associated with the mineral corundum.
The localities at which the chlorites occur are so numerous that even all of
the most important cannot be mentioned here. In the United States
corundophilite occurs at Chester, Mass., and Asheville, N. C.; pyrochlorite
at Foundryrun, Georgetown, D. C., and at Batesville, Va.; penninite at
Magnet Cove, Arkansas; and clinochlore at West Chester, Penn.
Return to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |

Chlorite Schist, Sierra Nevada Range,
California |
|