
| SAPPHIRE MINERAL FACTS |  |
|
| The Gem and Mineral Collector's Photo Gallery by Nevada Outback |
|
. Sapphire Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: Al2O3
Colors: Various shades, white to gray, green, blues, purple, yellows, browns, pinks, etc.
Hardness:
9.0
Density:
3.95 to 4.1 Cleavage: None, but separation planes parallel to the basal plane common. Parting basal and rhombohedral, the latter giving nearly cubic blocks.
Crystallography: Hexagonal-Rhombohedral Luster:. Adamantine to vitreous luster. Transparent to opaque. Optics: (Refractive Index): w= 1.7690; e= 1.7598 |
|
|
 |
||
Identification and Diagnostics
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins: Sapphires are found associated with the rubies of Thailand and Sri Lanka. They occur also at Banskar in Cashmere, India - Cashmire sapphires being highly valuable and sought after. They are also mined at several locations in east Africa, including the Umba river in Tanzania. In the United States small sapphires of fine color are found in various localities in Montana, where they were first found in the river sands east of Helena when washing them for gold. They have since been found embedded in the rock of lamprophyre dikes. The rock is quarried and after exposure to the air for a time it gradually decomposes, setting the sapphires free. Sapphires are also found over an extensive area in central Queensland, Australia. Emery was formerly used also as an abrasive, but the majority of such uses are replaced either by silicon carbide or synthetic corundum. Return to the Mineral Collectors Information Page |
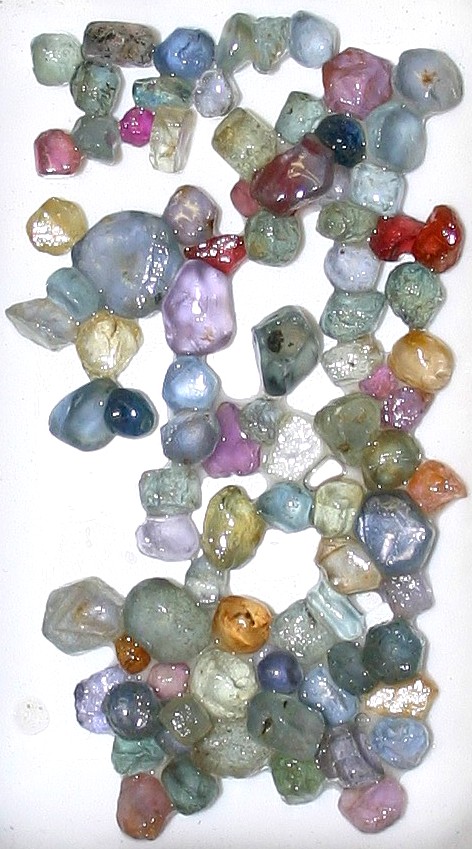

For More information about Sapphire as a gem, see:
|
|
|
|
||
 |
||
Please note that the author, Chris Ralph, retains all copyrights to this entire document and it may not be reproduced, quoted or copied without permission.
NEVADA OUTBACK GEMS TURQUOISE AND JEWELRY