|
.
Emerald (Beryl) Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: Be2Al2(SiO3)6
A trace of water is included.
Colors:
Emerald is the
Green to blue-green variety, and is colored by Chrome or Vanadium. Beryl can be colorless or of some light
shade of green, red, or blue. Its streak is white.
Hardness:
7.5 to 8.0
Hardness varies somewhat depending
on formation and impurities.
Density: 2.6
to 2.8
Cleavage:
Beryl's
cleavage is very imperfect but there is frequently a parting parallel to
the base.
Crystallography: Hexagonal
Strong
prismatic habit. The
usual form is in sharp and,
in some cases, very large columnar crystals with a distinct hexagonal
habit.
Crystals are frequently vertically striated and grooved. Forms usually
present consist only of prism of first order and base. Crystals can be
of considerable size with rough faces.
Luster:.
Beryl has a glassy
luster. It is transparent or translucent. Aquamarine is the name
given to the pale greenish blue transparent stone. Used as a gem or as a
collectors stone.
Optics:
(Refractive Index):
w= 1.5740, e= 1.5690
Pleochroism
is noticeable in green (emerald) and blue (aquamarine) crystals.
|
 |
|
Composition,
Structure and Associated Minerals:
Beryl is a frequent constituent
of coarse-grained granites. It is important as a gem material, and is
particularly interesting because of the many physical investigations that
have been made with the aid of its crystals. Although the mineral is
essentially a beryllium alumino-metasilicate, it usually contains also a
little Fe2O3
and MgO, in many
examples from pegamtites, small quantities of the alkalies, and in some
cases also caesium. The mineral occurs as an accessory constituent in
pegmatites and granites, in crystalline schists, especially mica schists and
gneisses. It is in these schists where the beryl can take up chromium from
adjacent rocks that most emeralds are formed.
Uses. The impure varieties are used
as an important ore of the Space-age metal Beryllium. The transparent
varieties are utilized as gems, under the following names:
Emerald is a deep green variety, the color is
due to Chromium or Vanadium.
Aquamarine, a blue-green variety, colored by
iron.
Golden beryl, a golden yellow-colored variety,
Morganite, a pink, high caesium variety, and
Gohenite or White beryl, a colorless variety.
Identification and Diagnostics
Beryl
whitens and fuses
with difficulty at 5-5.5 to an enamel. Yields a little water on intense
ignition. Insoluble in acids. Recognized usually by its hexagonal crystals,
its hardness, color, etc. Emerald is distinguished from other beryls by the
presence of chromium, vanadium or both.
Occurrence,
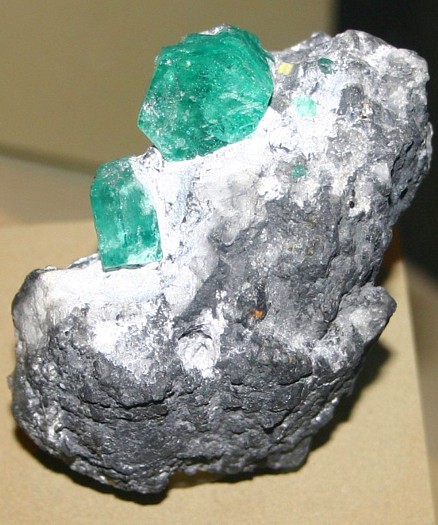
Localities and Origins (For Emerald):
Emerald beryl
colored by chromium or vanadium generally does not occur in the same types
of deposits as aquamarine, morganite or heliodor. This is because
those other environments do not allow the coloring agents needed for the
deep green of an emerald to come into the crystal. From ancient times up to
the 16th century, all emeralds were mined from deposits in Egypt, Austria or
Russia - all locations in the old world. All of these were deposits in
schist. After the discovery of the new world, emeralds began to come from
new sources and in much higher qualities. Columbia produces the world's
finest emeralds from a number of deposits in the state of Boyaca. The famous
Columbian emerald mines are found at Muzo, Chivoir, Cosquez, Gachala, and
Pena Blanca. All of these are unique low temperature veins situated in
sedimentary rocks and can produce emeralds of of a much higher quality and
size than those found in schist rocks. In recent years important emerald
production has come from several locations in Brazil (Santa Terezina,
Itabara and Carnaiba), the Transvaal in South Africa and Zambia.
All of these other sources are mines located in schist.
Return to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |
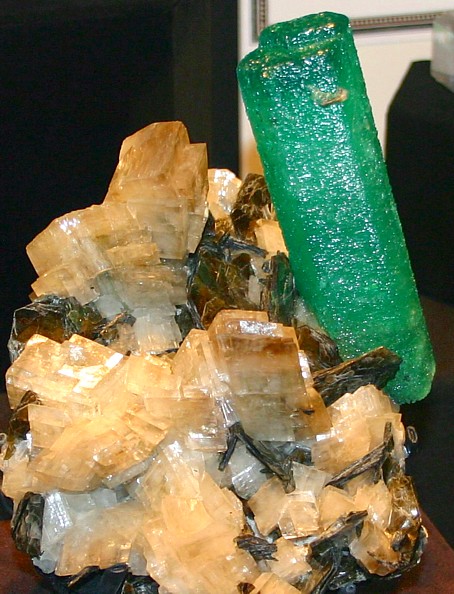

Emerald Crystal, North Carolina, USA |
|