|
.
Magnesite
Mineral Facts:
Chemical
Formula: MgCO3
Magnesium
carbonate, often some iron carbonate is normally present as an impurity.
Theoretically 47.6 percent magnesia.
Colors:
white,
gray, yellow, tan to brown.
Always has a white streak.
Hardness:
3.5 to 4.5
Density:
3 to 3.1
Cleavage:
Perfect rhombohedral
cleavage.
Crystallography:
Hexagonal
Compact earthy forms
common, also less frequently in cleavable granular masses, coarse to fine.
Also compact and massive. Well formed rhombohedral crystals rare.
Luster:.
Vitreous to earthy luster.
|
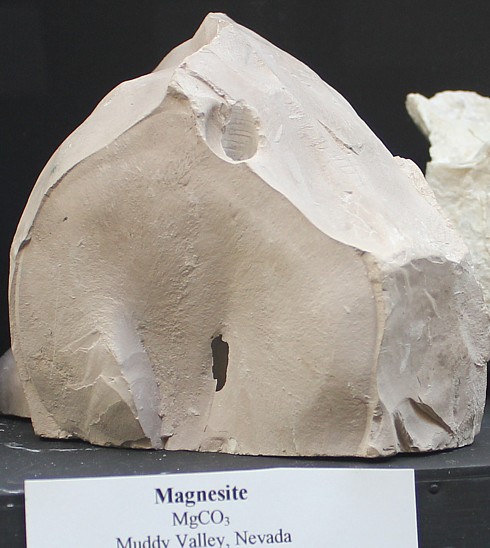

Magnesite magnesium ore, Nevada |
|
Composition, Structure and
Associated Minerals:
Magnesite
usually occurs in veins and masses associated with serpentine and other
magnesium rich rocks from which it has been formed by decomposition. It is
often accompanied by brucite, talc, dolomite and other magnesium compounds.
It has been described as occurring also in a distinct bed near Mohave, Cal.,
interstratified with clays and shales. It is thought that in this case it
may have been precipitated from solutions of magnesium salts by Na2CO.3. It
is mined commercially at Gabbs, Nevada as a magnesium ore using open pit
methods. Here it occurs at the contact of dolomite and a granitic intrusive
as a result of low pressure metamorphic changes.
Magnesite was mined to a small extent in Tulare County, California. Some of
the magnesite used in the United States is imported, coming chiefly from
Hungary and from Greece.
Identification
and Diagnostics
Magnesite behaves like
calcite
before the blowpipe. It effervesces in hot hydrochloric acid and readily
yields the reaction for magnesia with Co(NO3 )2. It is most easily
distinguished from the latter mineral by its density, by the fact that it
does not color the blowpipe flame with
the yellowish red tint of calcium and does not effervesce in cold HCl. After
intense ignition gives a faint alkaline reaction on moistened test paper.
Scarcely acted upon by cold but dissolves with effervescence in hot
hydrochloric acid. Solution, after the precipitation of any iron and
calcium, gives in the presence of an excess of ammonia, with sodium
phosphate, a white granular precipitate of ammonium magnesium phosphate
(positive test for magnesium).
Localities
The
mineral is found abundantly in many foreign localities, with the largest
deposits located in Greece and Hungary. In the US it is found at Bolton,
Mass.; Bare Hills, near Baltimore, Md., and in Tulare Co., Cal., and near
Texas, Penn.
It has been mined for decades along with
brucite
at Gabbs, Nevada.
Industrial Uses of
Graphite
Magnesite is the chief ore of the metal magnesium and
is mined extensively for a number of purposes in addition to the manufacture
of the metal. Magnesium metal is used in aircraft and other light
alloy materials.
Magnesite is
employed very largely in the manufacture of magnesite bricks used for lining
converters in steel works, in the lining of kilns, etc., in the manufacture
of paper from wood pulp, and in making, artificial marble, tile, etc. From
it are also manufactured epsom salts, magnesia (the medicinal preparation),
and other magnesium compounds, and the carbon dioxide used in making soda
water.
.Return
to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |
|