|
.
Topaz Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: Al2(F,OH)2SiO4
The mineral has a
varying composition, with variable portions of Fluorine and hydroxide
ions.
Colors: The
mineral is colorless, honey yellow, yellowish red, rose and rarely
bluish.
On prolonged exposure the
sunlight many of the color varieties eventually fade.
Streak is colorless or white.
Hardness:
8
Density:
3.52 to 3.57
Cleavage:
Perfect
parallel to the basal plane
{001}.
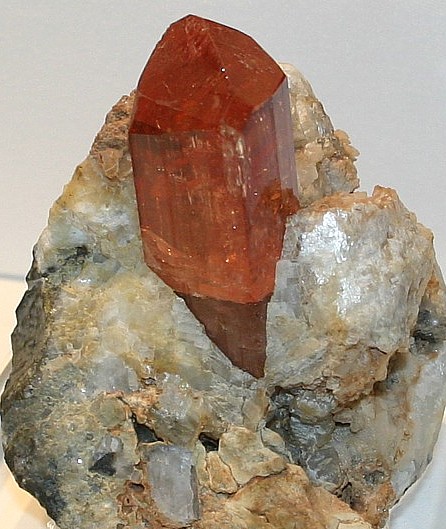
Crystallography: Orthorhombic
Occurs in
prismatic crystals terminated by pyramids, domes and basal plane. Often
highly modified and with prism faces often vertically striated. They are
notable for the number of forms that have been observed on them,
especially in the prismatic zone and among the brachypyramids.
Luster:.
Vitreous luster,
transparent to translucent.
Optics:
(Refractive Index): = 01=1.6294, 18=1.6308,
7=1.6375
Variable, depending on relative F to OH abundance.
|
 |
.
|
Composition,
Structure and Associated Minerals:
Topaz
occurs in igneous rocks, granites, rhyolites, etc., and good crystals are
found projecting into the druses, as in the Mourne Mountain granite, and in
the lithophysal cavities of rhyolites, as in Colorado. It is also a mineral
which occurs in tin-bearing pegmatites and in tin
veins generally, formed
through the agency of fluorine bearing
pneumatolytic fluid
vapors given off during the
last stages of the solidification of igneous rocks.
In these environments it is
found in cavities in rhyolite lavas and granite
associated with related minerals including
fluorite,
cassiterite, and
tourmaline,
apatite, etc. Topaz is also found associated in pegmatites with
quartz, mica,
feldspar. Because it is highly durable and hard, it is found at times in
alluvial deposits as water rolled pebbles in stream sands.
Identification and Diagnostics
Recognized chiefly by its crystal forms,
its basal cleavage, its unusual hardness of 8, and it's high specific
gravity. The mineral is distinguished from yellow quartz by its
crystallization, its greater hardness and its easy cleavage.
Topaz is infusible
before the blowpipe and is insoluble in acids. The powdered mineral, when
heated, moistened with cobalt nitrate and reheated, assumes a blue color,
due to aluminum. Fused with microcosmic salt, gives off silicon fluoride,
which etches the glass. At a high temperature it loses its fluorine as
silicon and aluminum fluorides. The mineral also can exhibit pyroelectrical
properties, but these are apparently distributed without regularity in
different crystals. Many crystals contain inclusions of fluids containing
bubbles, and sometimes of two immiscible fluids which are normally gaseous
carbon-dioxide and liquid water.
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins:
The mineral
occurs principally in pegmatites, in gneisses, and in acid volcanic rocks.
In all cases it is probably the result of the escape of fluorine-bearing
liquids and gases emanating from cooling igneous magmas. Topaz is found in
handsome crystals at Schneckenstein in Saxony, in a breccia made up of
fragments of a tourmaline-quartz rock cemented by topaz. It occurs also in
the pegmatites of the tin mines in Ehrenfriedersdorf, Marienberg and other
places in Saxony, Bohemia, England, etc.; on the walls of cavities in a
coarse granite in Jekaterinburg and the Ilmengebirge, Russia;
in pale blue crystals from
Adunchilon and Mursinka in Siberia, the Mino Province, Japan;
in veins of kaolin
cutting a talc schist in Minas Geraes in Brazil;
and in the cassitefite-bearing
sands at San Luis Potosi, Durango and other points in Mexico.
Imperial topaz is the rarest
and most desirable gem topaz variety, with its shades peach, pink, orange or
champagne colors. Most production comes from the mines of Ouro Preto in
Minas Gerais, Brazil, but the first deposits were found in the Ural
Mountains of Russia.
It is named for the Imperial Russian Monarchy. Some pale pink topaz comes
from Afghanistan. In the United States it occurs on the walls of cavities in
acid volcanic rocks, at Nathrop, Colo., in the Thomas Range, Utah, and other
places. It occurs also in veins with muscovite, fluorite, diaspore and other
minerals at Stoneham, Maine, and Trumbull, Conn. Blue Crystals are found in
Mason County Texas. It is found associated with amazonite feldspar at a
location near Hawthorne, Nevada and in the Pike's peak area of Colorado.
The
principal use of topaz is as a gemstone, though large and showy specimens
are also prized by mineral collectors. Some very large crystals are
occasionally available that are capable of producing gems more than two
thousand carats in weight. Because of its toughness and hardness, it makes
for an excellent gem for daily wear.
Historically, a number
of other inferior stones like quartz were once also frequently called topaz.
Trade laws have outlawed this old practice. The color of the stones varies,
being colorless, wine-yellow, golden brown, pale blue and pink. Most of blue
colored material seen in jewelry stores is colorless material that has been
irradiated. Irradiation produces colors ranging from sky to deep blues. The
material has no long term radioactivity, and there are testing procedures to
make sure the gems are safe. The pink color is usually artificial,
being produced by gently heating the deep orange yellow imperial colored
stones. The color change is permanent, however.
For more information on this gem, see:
Topaz
- The many colored Gem
Return to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |
 |
|