|
.
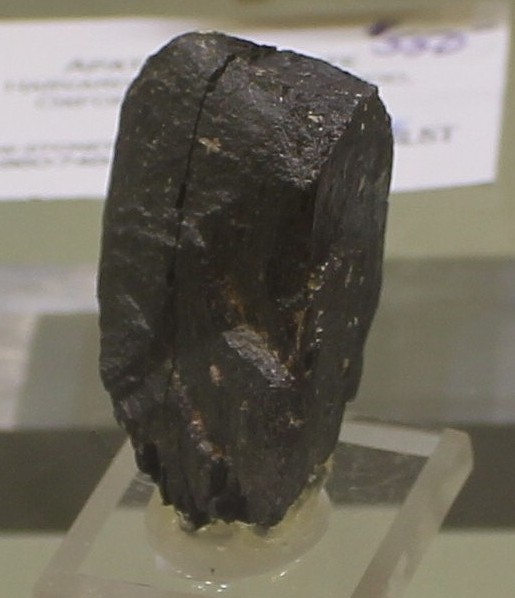
Columbite
Mineral Facts:
Chemical
Formula: (Fe,Mn)Nb2O6
The niobate
of ferrous iron and manganese. The mineral often contains small amounts of
tin, tungsten, tantalum, etc.
Colors:
iron-black,
frequently iridescent.
The streak is dark red to black.
Hardness:
6
Density:
5.3 to 7.3
Density is variable based on chemical make up and amounts of impurities.
Cleavage:
The cleavage is
distinct parallel to (010).
Crystallography: Orthorhombic
Habit of crystals is
short prismatic; often in square prisms because of prominent development of
the vertical pinacoids. Terminated by basal plane, pyramids and domes;
frequently
complex. At times in heart-shaped contact twins. Crystallized and in
parallel crystal groups. It is also frequently granular and massive.
Luster:.
submetallic luster.
|

Columbite Niobium ore |
|
Composition, Structure and
Associated Minerals:
Columbite occurs in
granite rocks and in pegmatite veins, associated with
quartz, feldspar, mica,
tourmaline,
beryl,
spodumene,
casseterite, samarskite,
wolframite, microlite,
monazite, etc. Notable
localities for its occurrence are the west coast of Greenland; Bodenmais,
Bavaria; llmen Mountains, Siberia; Western Australia (manganotantalite);
Standish, Maine; Haddam, Middletown and Branchville, Connecticut; in Amelia
County, Virginia; Mitchell County, North Carolina; Black Hills, South
Dakota; near Canon City, Colorado. Some specimens
exhibit weak radioactivity.
Identification
and Diagnostics
Columbite is infusible before the
blowpipe. Composition variable, When columbite is decomposed by
fusion with borax; the bead dissolved in hydrochloric acid; the solution
boiled with tin gives a blue color ( positive test for niobium). The mineral
is also partially decomposed
when evaporated to dryness with H2SO4, forming a white compound that changes
to yellow. When this residue is boiled with HC1 and metallic zinc a blue
solution results. The mineral also gives reactions for iron and manganese.
There is no simple test for tantalum. Generally when fused in 0xidizing
flame with sodium carbonate it gives an opaque bluish green bead. Fused with
sodium carbonate on charcoal in R. F. yields a magnetic mass. Recognized
usually by its black color, submetallic streak and high specific gravity.
Columbite may easily be confused with black tourmaline, ilmenite and
wolframite. From tourmaline, they are distinguished by crystallization, high
specific gravity and luster; from
wolframite by their less perfect cleavage and by the reaction with aqua
regia; from ilmenite by the test for titanium.
Localities
Columbite is
found in granite veins at Bodenmais, Germany; Tammela, in Finland; near
Limoges, France, with tantalite; near Miask,
in the Ilmen Mountains, Russia, with samarskite; and at Ivigtut, in
Greenland. In the United States it is found at Standish and Stoneham,
in Maine; at Acworth, in New Hampshire; at Haddam, in Connecticut; at Amelia
Court House, Virginia; with samarskite in the mica
mines in Mitchell County, North Carolina; in the Black Hills, South Dakota,
San Diego County California and at a number of other points in New England
and the western USA.
.Return
to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |
|