
| BENITOITE MINERAL FACTS |  |
|
| The Gem and Mineral Collector's Photo Gallery by Nevada Outback |
|
.Benitoite Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: BaTiSi3O9
Colors:
Colorless to deep blue. Hardness: 6.5 Density: 3.6 Cleavage: No cleavage. Conchoidal fracture.
Crystallography: Hexagonal Luster:. Vitreous luster, transparent to translucent, with a high dispersion and refractive index. Optics: (Refractive Index): = 1.76 |
|
|
 |
||
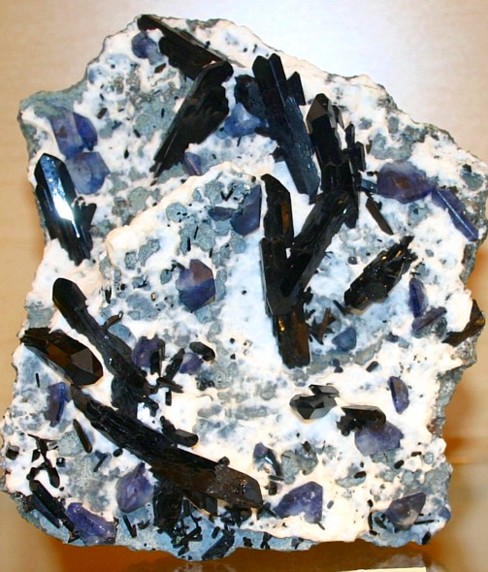
Benitoite is a rare mineral found in very few locations across the world. known localities include San Benito and Santa Cruz Counties in California, as well as Japan and Arkansas. In the San Benito occurrence, it is found in natrolite veins within a glaucophane schist interlayered with a serpentine body. The Benitoite or Dallas Gem mine, located at the head waters of the San Benito river, is the type locality. In Japan, the mineral occurs in a magnesio-riebeckite-quartz-phlogopite-albite dike cutting a body of serpentinite. In 1985 benitoite was approved by the legislature as the official state gem of California. The crystals are formed in fractures of a serpentine rock and deposited from hydrothermal solutions. These hot solutions contained a number of unusual elements dissolved within them, including barium, titanium, fluorine, iron, cesium, niobium, manganese and lithium in relatively high concentrations. The causes of such a solution and what other conditions caused the crystallization of these rare minerals is still not well understood.
Identification and Diagnostics
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins: The attractive clusters of blue benitoite and black neptunite associated with a crust of white natrolite produce a truly desirable mineral combination that is a must have for all serious mineral collectors. The white natrolite covers over the crystals in most specimens, but is soluble in acids, and so most specimens have been treated with acid to better expose the beautiful benitoite and neptunite crystals. At the time of this writing, the old Dallas Gem mine site has been made open to collectors to work the dumps of previous operations for a fee. Some nice specimens have been collected in recent years, but the price to hunt is not cheap. For information on gem Benitoite, see: Benitoite - The California Gem Return to the Mineral Collectors Information Page |
 |
|
 |
|
|
Please note that the author, Chris Ralph, retains all copyrights to this entire document and it may not be reproduced, quoted or copied without permission.
NEVADA OUTBACK GEMS TURQUOISE AND JEWELRY