|
.
Manganite
Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: (MnO)OH
In addition to
the basic manganese oxide constituents, the mineral commonly contains also
some iron, magnesium, calcium and often traces of other metals.
Colors:
Steel gray to
iron-black,
frequently iridescent.
The streak is dark
reddish brown to nearly black.
Hardness:
4
Density:
4.3
Cleavage:
The cleavage is
perfect parallel to (010) on (110)
and (001) the cleavage is
good.
Crystallography:Monoclinic; Psudo-Orthorhombic
Habit of crystals is
Manganite usually occurs in groups of black columnar or prismatic crystals
and in stalactites. The prismatic surfaces are deeply striated vertically
and the crystals are often in bundles with obtuse terminations. It is also frequently
found in fiberous and massive forms.
Luster:.
submetallic luster.
It is usually
opaque but in very thin splinters it is sometimes red-brown by transmitted
light. |
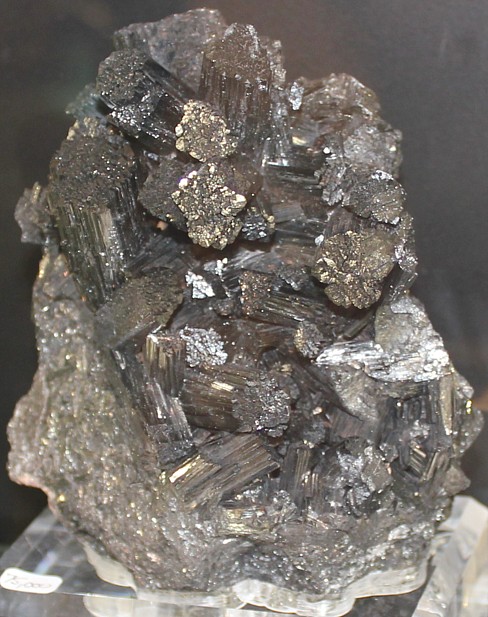

Manganite Manganese ore |
|
Composition, Structure and
Associated Minerals:
Manganite commonly occurs with other
manganese oxides in secondary deposits formed by circulating meteoric water
where manganese has been leached by weathering in environments of clays and
laterites. It also forms by low temperature hydrothermal action in metal
bearing veins in association with
calcite,
barite, and
siderite. It is often associated with
pyrolusite, braunite, hausmannite and
goethite.
The mineral is a nonconductor
of electricity.
Identification
and Diagnostics
Manganite
is infusible in
the blowpipe flame,
yields water in the closed tube
and colors the borax bead amethyst in the oxidizing flame of the blowpipe
(test for manganese).
The borax bead
test is the same as for pyrolusite.
In the reducing flame, upon
long-continued heating, this color disappears. The mineral dissolves in
hydrochloric acid with the evolution of chlorine. It is distinguished from
other manganese minerals by its hardness and crystallization. By loss of
water manganite passes readily into
pyrolusite (MnO2).
It also readily alters into other manganese compounds.
Manganite
is dentified
chiefly by its
black color, prismatic crystals, hardness (4) and brown streak. The last two
will serve to distinguish it from pyrolusite.
Occurrence,
Localities and Origin.
Found in connection with
pyrolusite and other manganese minerals and with iron oxides.
Manganite occurs both in veins in old volcanic rocks, and also in limestone.
It is found at Ilfeld in the Harz; at Ilmenau in Thuringia, and at Langban
in Sweden, in handsome crystals. In the United States it occurs at the
Jackson and the Lucie iron mines, Negaunee, Michigan, and in Douglas County,
Colorado. It is also abundant at various places m New Brunswick and Nova
Scotia. In all cases it is a residual product of the weathering of manganese
compounds. It is a minor manganese ore mineral. Manganite is used in the
production of manganese compounds. As mined, it is usually mixed with
pyrolusite, this being the most important portion of the mixture.
.Return
to the
Mineral Collectors Information Page |
|