
| PYRITE MINERAL FACTS |  |
|
| The Gem and Mineral Collector's Photo Gallery by Nevada Outback |
|
.Pyrite Mineral Facts:
Chemical Formula: FeS2
The Mineral is 46.6% Iron by weight. Colors: Pale brass yellow on fresh surface, tarnishing to a darker shade. Streak: greenish or brownish black.
Hardness:
6.0 to 6.5
(This is
unusually hard for a sulphide) Cleavage: The cleavage is imperfect and its fracture conchoidal. The mineral is brittle.
Crystallography:
Isometric: Cubic Luster:. Metallic, Its luster is very brilliant and splendent. Optics: (Refractive Index): a = 1.730; b = 1.758; y = 1.838 |
|
|
| . | ||
Composition,
Structure and Associated Minerals: Pyrite in some of its forms so closely resembles gold that it is often known as fool's gold. There is, of course, no difficulty in distinguishing between the two minerals, since pyrite contains sulphur and is soluble in nitric acid, while gold contains no sulphur and is insoluble in all simple acids. Pyrite occurs in quartz veins and as grains or crystals embedded in all kinds of rocks. In rocks it usually appears as crystals, but in vein-masses it may appear either as crystals, with other minerals, or as radiating or structureless masses occupying entirely the vein fissures. In slates it often occurs in spheroidal nodules and concretions of various forms, and also as embedded crystals. The mineral is the product of igneous, metamorphic and aqueous processes. Pyrite weathers readily to limonite. In ore bodies near the surface it is oxidized. A portion of the mineral changes to FeSO4 which percolates downward and aids in the concentration of any valuable metals that may be present in small quantity in the ore. Another portion of the iron remains near the surface in the form of limonite. This covering of oxidized material is known as the "gossan" and it is characteristic of all pyrite deposits. Pyrite is often mined as a gold ore, and sometimes for the copper associated with it. Because of the large amount of sulfur present in the mineral it is never used as an iron ore.
Identification and Diagnostics
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins: Massive pyrite occurs in great deposits at the Rio Tinto mines in Spain; at Rowe, Mass.; in St. Lawrence and Ulster counties, N. Y.; in Louise Co., Va., and in Paulding Co., Ga. Much of the massive pyrite in the veins of Colorado, California and of the southern states, from Virginia to Alabama, is auriferous and is mined for the gold it contains. Gold is separated from the pyrite partly by crushing and amalgamation and partly by smelting or by leaching processes. Within the pyrite crystals, gold occurs as inclusions of the metal. Pyrite is used principally in the manufacture of sulphuric acid. The mineral is burned in furnaces and the SO2 gases thus resulting are carried to condensers where they are oxidized by finely divided platinum or by the oxides of nitrogen. The residue, which consists largely of FeO2, is sometimes smelted for iron or made into paint. This residue sometimes also contains the gold and other valuable metals that may have been in the original pyrite. The sulphuric acid obtained from pyrite enters into many manufacturing processes. The greater portion of it is consumed in the artificial fertilizer industry. Return to the Mineral Collectors Information Page |
Pyrite, with Quartz, California Mother Lode |
|
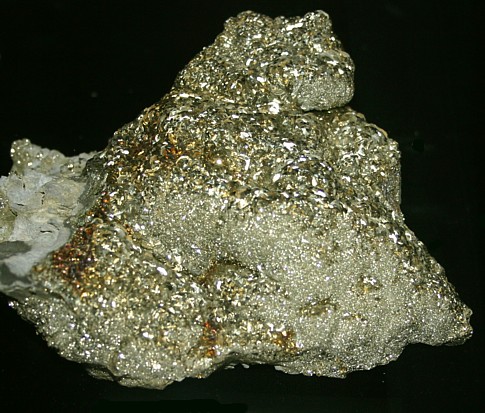 Pyrite aggregate mass, Carlin District, Nevada |
||
Please note that the author, Chris Ralph, retains all copyrights to this entire document and it may not be reproduced, quoted or copied without permission.
NEVADA OUTBACK GEMS TURQUOISE AND JEWELRY