
| GALENA MINERAL FACTS |  |
|
| The Gem and Mineral Collector's Photo Gallery by Nevada Outback |
|
. Galena Mineral Facts: Chemical Formula: PbS The Mineral is 86.6% Lead by weight.
Colors:
Lead -gray on fresh surfaces.
Streak: gray Density: 7.4 to 7.6 Cleavage: {001} perfect cleavage parallel to the cubic faces.
Crystallography: Isometric: Cubic Optics: (Refractive Index): opaque |
An Aggregate of Galena Crystals |
|
|
|
||
Galena weathers readily to the sulfate (anglesite) and carbonate (cerussite) ; consequently it is usually not normally found in the upper portions of veins that are exposed to the action of the air. Veins of galena containing silver (silver-lead) are probably produced by ascending hot water solutions emanating from bodies of igneous rocks, while the galena in limestone was probably deposited by groundwater that dissolved the sulfide from the surrounding sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Galena occurs very widely spread. It is found in veins associated with quartz, calcite, barite or fluorite and various sulfides, especially sphalerite; in irregular masses filling clefts and cavities in limestone; in beds, and in stalactites and other forms characteristic of water deposits. It occurs also as pseudomorphs after pyromorphite the lead phosphate. The form that occurs in veins is often silver bearing, while that in limestone is usually free from silver.
Identification and Diagnostics
Occurrence,
Localities and Origins: Galena occurs most commonly in connection with limestones, either as veins or irregular deposits, or as replacement deposits. The following are the important lead producing localities in the United States: Southeastern Missouri, in which the ore occurs in the form of beds with the mineral disseminated through the limestone; southwestern Missouri, where it is associated with zinc ores, and is found in irregular veins and pockets in limestone and chert. In these southern districts the galena is associated with sphalerite, pyrite, smithsonite, calamine, cerussite, calcite and other minerals, fills cavities in limestone. In the western US, where the lead is derived chiefly from lead-silver deposits, locations include Idaho, where the greater part of which come from the Coeur d'Alene region near Wallace in Shoshone County; Utah, in connection with the silver deposits of the Tintic and Park City districts; Colorado, chiefly from the lead-silver ores of the Leadville District, at various points in Montana; and at many other places in the Rocky Mountain region. In Nevada, the Eureka district was long a major lead producer. The most famous foreign localities are, Freiberg, Saxony; the Harz Mountains; Pfibram, Bohemia; Cornwall, Derbyshire and Cumberland, England. The name galena is derived from the Latin galena, a name originally given to lead ore. It is practically the only source of lead and an important ore of silver. Metallic lead is used chiefly for batteries, as a weight, for bullets, radioactive shielding and low-fusion alloys consisting of lead, bismuth and tin. Its most important alloys include solders, pewter and babbitt metal. Return to the Mineral Collectors Information Page |
Galena Cubes |
|
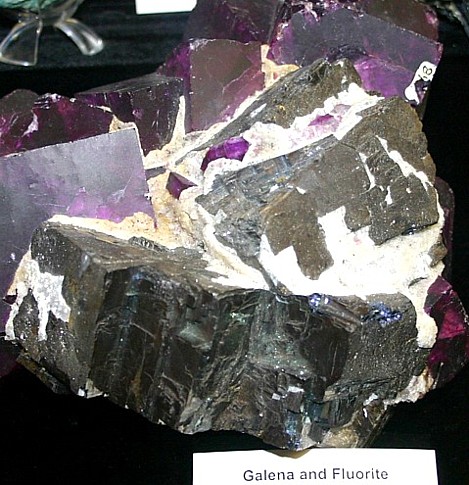 Fluorite (purple) and Galena (Gray) Crystals |
||
Please note that the author, Chris Ralph, retains all copyrights to this entire document and it may not be reproduced, quoted or copied without permission.
NEVADA OUTBACK GEMS TURQUOISE AND JEWELRY